Hazardous Area Zones | Zone 1 & Zone 2 | An Explanation Guide to Explosive Atmospheres

Thorne & Derrick’s in-depth guide to understanding Hazardous Area Zones, Definitions, Classifications & Products.
We’re not just experts in the industry… Thorne & Derrick International are Specialist Distributors of Hazardous Area Electrical, HVAC & Process Instrumentation Equipment to UK and international projects.
Leaders in the development and distribution of ATEX & IECEx Product Innovations that deliver significant improvements to clients plant, people and operational safety in the explosive atmosphere industries.
Contact our experts – find out more about Hazardous Area Zones & Products, and why they may be crucial for your operations.
Your first-choice provider and proactive problem solvers, experienced in succession planning for the replacement of obsolete, non-conformant and legacy equipment in hazardous areas.
Hazardous Area Zones Explained
Hazardous area zones are classified based on the likelihood and duration that explosive gases, vapours, or dusts may be present. Correct classification ensures the safe installation of electrical and mechanical equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres and compliance with ATEX and IECEx standards.
Read more about hazardous area classifications
In many industrial environments, processes can lead to the presence of flammable gases, vapours, and dusts. When combined with electrical equipment, these can pose significant explosion risks. International standards such as ATEX and IECEx govern how hazardous areas are classified and how certified equipment should be used safely.
Hazardous areas are divided into Zones based on the likelihood of an explosive atmosphere being present. These classifications help engineers select equipment certified to the correct protection level. The standards IEC 60079-10-1:2015 (gas) and IEC 60079-10-2:2015 (dust) define these zones internationally. Proper classification supports safe plant design, operational reliability, and explosion protection compliance.
Gas & Vapour Hazardous Area Zones
Gas and vapour zones are classified according to how frequently an explosive gas atmosphere is present. These zones apply to areas handling hydrocarbons, solvents, or flammable vapours—such as refineries, LNG plants, paint booths, and fuel storage facilities.
Zone 0: These areas have an explosive gas atmosphere continuously or for long periods. Examples include the interior of storage tanks or sumps where flammable liquids are stored. Equipment used here must meet Category 1G under ATEX and be safe even in the event of rare faults. Typical protection types include Ex ia (intrinsic safety) or Ex ma (encapsulation).
Zone 1: These areas are those where explosive atmospheres are likely to occur in normal operation. These zones are found near pumps, valves, flanges, or other components prone to leaks. Equipment must be certified to Category 2G and commonly employs Ex d (flameproof), Ex e (increased safety), or Ex p (pressurisation) protection concepts.
Zone 2: Areas where explosive gas atmospheres are unlikely in normal operation and, if they occur, only persist for short durations. Common examples include well-ventilated pump rooms or open plant areas adjacent to Zone 1 equipment. Equipment certified to Category 3G is suitable here, typically with Ex n or Ex ec protection.
Dust Hazardous Area Zones
Dust zones apply where combustible powders or fibres can form explosive atmospheres when dispersed in air. Industries such as food processing, woodworking, pharmaceuticals, and metal finishing frequently encounter these risks.
Zone 20: These areas contain combustible dust clouds continuously or for long durations. Examples include the interiors of silos, filters, or dust collectors. Equipment installed must be certified to Category 1D and designed to prevent ignition from overheating or electrical discharge.
Zone 21: These locations experience explosive dust atmospheres intermittently during normal operation. Typical examples include powder transfer stations, bagging plants, or conveyor discharge points. Equipment must meet Category 2D and typically uses Ex tD (protection by enclosure) or Ex pD (pressurisation) methods.
Zone 22: Represents areas where explosive dust atmospheres are unlikely and short-lived. Common examples include warehouse areas, processing plant surroundings, or areas near dust extraction ducts. Equipment used here must be certified to Category 3D and have surfaces kept below ignition temperatures.
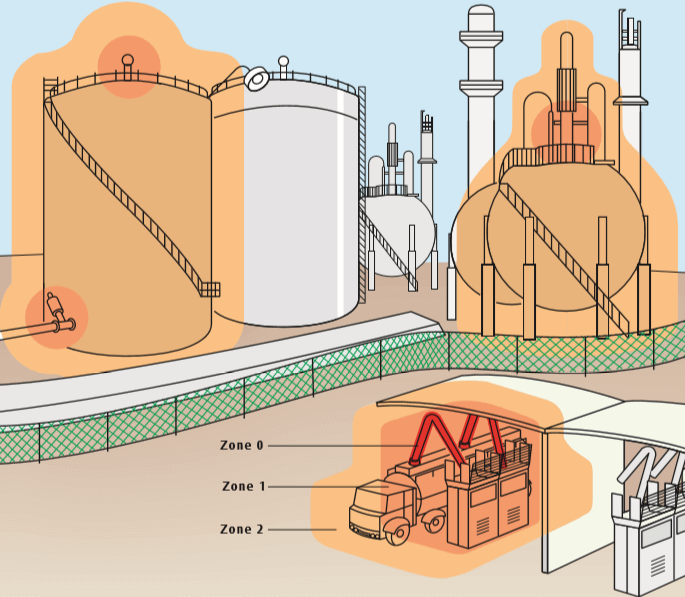
Diagram: Hazardous Area Zones 0, 1, 2 and Dust Zones 20, 21, 22
International Hazardous Area Classifications
Several international certification schemes govern equipment used in explosive atmospheres. Understanding their distinctions ensures global compliance and safety across hazardous area installations.
- IECEx: International Electrotechnical Commission certification system for equipment used in explosive atmospheres.
- ATEX: European Directive ensuring electrical and mechanical equipment is designed to prevent ignition in explosive environments.
- CSA: Certification for explosion-proof and intrinsically safe equipment used in hazardous locations across North America.
- EAC Ex: Customs Union certification for equipment safety in explosive atmospheres (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan).
- INMETRO: Brazilian certification ensuring electrical equipment is safe for use in hazardous atmospheres.
Read more about global Ex standards
Each certification system has specific testing protocols, documentation, and marking requirements. Compliance with international standards enables manufacturers and operators to ensure consistent safety performance, traceability, and legal conformity across global hazardous area installations.

Hazardous Area Electrical, HVAC & Process Instrumentation Equipment | IECEx, ATEX, INMETRO, GOST & EAC
Hazardous Areas & DSEAR
The Dangerous Substances and Explosive Atmospheres Regulations 2002 (DSEAR) establishes legal requirements to manage and control fire and explosion risks from dangerous substances in the workplace. DSEAR forms the foundation of UK hazardous area safety, aligning closely with ATEX and IECEx international standards for explosive atmospheres.
Read more about DSEAR regulations
DSEAR uses the term “dangerous substances” rather than “flammable substances,” broadening its scope beyond IEC or CENELEC definitions. The regulations require employers to assess, control, and eliminate risks where explosive atmospheres could form.
DSEAR applies whenever:
- Work is undertaken by an employer or self-employed person.
- A dangerous substance is present, used, or produced.
- The substance poses a risk of fire, explosion, or similar energetic event.
DSEAR covers all types of workplaces — including industrial plants, offshore installations, chemical processing facilities, construction sites, and vehicles — where flammable liquids, vapours, gases, or dusts may be found.
Preventing & Controlling Risks in Hazardous Areas
Employers must take measures under DSEAR to eliminate or minimise risks arising from dangerous substances as far as reasonably practicable. Where full removal of risk is impossible, suitable control measures must be implemented to reduce the consequences of any fire or explosion.
Read more about risk prevention and control
The most effective strategy is substitution — replacing a hazardous substance with a safer one or modifying processes to reduce danger.
Examples of effective control measures include:
- Reducing the quantity of dangerous substances in use or storage.
- Preventing the release of flammable vapours, gases, or dusts.
- Ensuring adequate ventilation to prevent explosive atmospheres forming.
- Containing or venting accidental releases to a safe location.
- Eliminating ignition sources through certified equipment and strict maintenance.
Hazardous Areas Under Control
Hazardous area classification forms an essential part of a site’s risk assessment strategy. By identifying and zoning areas where explosive atmospheres could occur, engineers can ensure certified equipment is selected and ignition sources are effectively controlled.
Read more about hazardous area control and classification
Zones are determined based on the frequency and duration of explosive atmospheres being present. This process ensures compliance with ATEX and IECEx standards.
Benefits of full hazardous area classification include:
- Cost Savings – Reduces redundant testing and speeds access to markets.
- Improved Safety – Ensures compliance with international explosion protection standards.
- Instant Verification – ATEX and IECEx markings demonstrate suitability for use in hazardous areas.
Hazardous Area Directives | ATEX & IECEx
International directives such as ATEX and IECEx ensure consistent global standards for electrical and mechanical equipment used in explosive atmospheres. These certification systems enhance workplace safety, simplify compliance, and promote equipment interoperability worldwide.
ATEX Certification
The ATEX Directives – Equipment Directive 94/9/EC (ATEX 95) and Workplace Directive 1999/92/EC (ATEX 137) – define requirements for equipment and workplaces exposed to explosive atmospheres. ATEX applies to environments containing flammable gases, vapours, or combustible dusts.
Read more about ATEX certification
ATEX 95 ensures equipment meets unified EU standards. Equipment is grouped as follows:
- Group I – Equipment for underground mines.
- Group II – Equipment exposed to explosive gases or vapours.
- Group III – Equipment exposed to combustible dusts.
ATEX 137 focuses on workplace zoning: Zone 0, 1, 2 (gases) and Zone 20, 21, 22 (dusts).
Derived from the French ATmosphére EXplosif, ATEX has been mandatory across Europe since June 2003, harmonising safety and trade across the EU.
IECEx Certification
The IECEx Certification System facilitates the global acceptance of product safety test results for equipment used in explosive atmospheres. Endorsed by the United Nations, IECEx ensures consistent international standards for explosion protection.
Read more about IECEx certification
IECEx eliminates duplicated testing, allowing equipment to be certified once and accepted globally. It covers electrical and non-electrical equipment, installations, and repair services.
Other recognised international certifications include:
- INMETRO – Brazil
- GOST – Russia & Ukraine
- NEC – North America
Together, these frameworks form a globally harmonised system for hazardous area classification and certification, ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance across industries.
Find out more about IECEx Certification with this in-depth guide.
Our Hazardous Area Product Categories
ATEX Lighting
ATEX lighting provides certified illumination for hazardous areas where explosive gases, vapours, or dusts may be present. Designed for Zone 1 / Zone 2 (gas) and Zone 21 / Zone 22 (dust) environments, these luminaires meet ATEX and IECEx standards to ensure safety and reliability in demanding industrial settings.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Raytec | Petrel | Appleton
- Fluorescent or LED: Emergency, bulkhead, well glass, and floodlight fittings
- Portable: Handlamps, torches, headtorches, and floodlights for inspection and maintenance
- Temporary Lighting: Tanklights, airlamps, and mobile floodlighting systems
Control Panels & Distribution Boards
Hazardous area control panels and distribution boards are designed for safe, reliable operation in Zone 1, Zone 2, Zone 21 and Zone 22 explosive atmospheres. Certified to ATEX and IECEx standards, these enclosures provide flameproof (Ex d), increased safety (Ex e) and Ex de protection for power, control, and instrumentation circuits.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: P+F | Abtech
- Electrical Distribution Panels: Certified for safe LV and HV power management in hazardous areas
- Lighting & Heat Tracing Panels: For controlled illumination and process heating systems
- Machine Control Switchboards: Built to customer specifications with integrated protection devices
- Battery Boxes & Containers: Explosion-proof energy storage and power back-up solutions

Control Stations & Push Buttons
Hazardous area control stations are engineered for reliable operation in Zone 1 / Zone 2 (gas) and Zone 21 / Zone 22 (dust) environments. Certified to ATEX and IECEx standards, they provide safe switching and emergency control in explosive atmospheres.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: P+F | CEAG | Technor
- Ex ed IIC T4
- Ex e II T4
- Emergency Stop Station: For rapid system shutdown in critical safety situations
- Emergency Power Off: Immediate power isolation for hazardous operations
- Stop/Start Stations: Simple operator control with integrated safety functionality
- Custom Configurations: Bespoke assemblies with express delivery available

Signalling (Sounders & Beacons)
Hazardous area sounders and beacons provide reliable audible and visual alerts in explosive gas and dust environments. Certified to ATEX and IECEx standards, these sounders, beacons, and strobes are essential for safety, fire, and gas detection systems in onshore, marine, and offshore applications.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: EATON | CEAG | Technor
- Sounders: High-output alarm horns and loudspeakers for industrial warning systems
- Beacons: Flashing or steady signal lights with LED or xenon strobes
- Manual Alarm Call Points: ATEX-certified units for fire and emergency alarm activation
![]()
Isolators & Switch Disconnectors
Hazardous area isolators and switch disconnectors provide safe circuit isolation in Zone 1 and Zone 2 explosive atmospheres. Certified to ATEX and IECEx standards, they are available in Ex d (flameproof) or Ex e (increased safety) versions with 16A–250A ratings and 3–4 pole configurations.
Manufactured from cast iron or cast aluminium, these isolators provide reliable performance in demanding industrial environments including chemical, oil and gas facilities.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Craig & Derricott | CEAG
- Hazardous Area Certification: Ex d II 2 GD IIB T4, T5 or T6
Enclosures & Junction Boxes
ATEX enclosures and junction boxes are designed for Zone 1 / Zone 2 (gas) and Zone 21 / Zone 22 (dust) applications, ensuring safe power distribution, termination, and control in explosive atmospheres. Certified to ATEX and IECEx standards, they are available in stainless steel, aluminium, GRP, and polycarbonate constructions.
Options include flameproof Ex d, increased safety Ex e, and high voltage enclosures up to 33kV for jointing and termination of power cables in Zone 2 hazardous areas.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Abtech | CEAG
- Flameproof Ex d Electrical Enclosures & Junction Boxes
- Increased Safety Ex e Electrical Enclosures & Junction Boxes
- High Voltage ATEX Certified Enclosures 3.3kV–33kV

Plugs & Sockets
Hazardous area plugs and sockets provide safe and reliable low-voltage power connections in explosive atmospheres. Certified to ATEX and IECEx, these Ex de explosion-protected decontactors are designed for Zone 1 & 2 (Gas) and Zone 21 & 22 (Dust) environments.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Marechal | CEAG | Appleton
Available in single pole, compact, or metal configurations, these connectors ensure mechanical strength, ingress protection, and safe disconnection under load.
- Single Pole Power Connectors – 680A, IK09, IP66, Ex e IIC
- Zone 1 & 2 Compact Plugs – 63A, IK09, IP66, Ex de IIC Gb
- Zone 1 & 2 Metal Plugs – 200A, IK10, Ex de IIC

Electrical Heating
Hazardous area electrical heating systems deliver frost protection and process temperature control in explosive atmospheres. Designed for Zone 1 and Zone 2 applications, these ATEX and IECEx certified heaters maintain safe and efficient operation in critical industrial environments.
The range includes air (‘The Bulldog’ & LFH), immersion, water, and line heaters designed for oil, gas, and chemical industries, ensuring reliability in harsh or hazardous conditions.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: EXHEAT
- Air Heaters & Air Duct Heaters – Ex d & Ex e
- Immersion Heaters – Rod, Flanged & Removable Core
- Water Heaters – Point of Use & Bulk Storage
- Line Heaters – Maintain Process Liquid Flow

Drum & IBC Heaters
Hazardous area Drum Heaters and IBC Heaters maintain product temperature, reduce viscosity, and prevent frost damage in industrial storage and processing environments. Designed for use in Zone 1 and Zone 2 hazardous areas, they ensure safe and uniform heat distribution.
Available for 205-litre drums and 1000-litre IBC containers, these flexible electrical heating jackets are ideal for chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Winkler | Eltherm | Heatfast
- Drum Heaters – Standard 205 Litre Drums
- IBC Heaters – Standard 1000 Litre Containers
- Customised Container & Drum Heaters – ATEX & IECEx Certified

Gas Detection
Gas detection systems ensure safe monitoring of flammable and toxic gases in hazardous areas. Portable and fixed gas detectors provide early warning of leaks and oxygen depletion in Zone 1 and Zone 2 environments, maintaining safety in confined and industrial spaces.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Crowcon
- Portable & Fixed Gas Detectors – ATEX & IECEx Certified
- Single Gas & Multi-Gas Detection – Flammable & Toxic Gases
- Applications: Oil & Gas, Petrochemical, and Manufacturing Plants

Heat Trace
Heat trace cable provides frost protection and temperature maintenance for process pipes, tanks, and equipment in hazardous areas. Designed for Zone 1 and Zone 2 explosive atmospheres, heat tracing ensures safe, energy-efficient operation across industrial, marine, and offshore environments.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Eltherm | Heatfast
- Self-Regulating Heating Cables – Pipe Frost Protection
- Constant Wattage & MI Cables – Process Heating
- ATEX & IECEx Certified Heat Trace Systems

Static Bonding Systems
Static bonding and grounding systems prevent static electricity buildup in explosive atmospheres. Designed for Zone 1 and Zone 2 hazardous areas, these systems safely dissipate electrostatic discharge during tanker loading, transfer, and blending operations.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Stuvex
- Static Grounding Clamps – ATEX & IECEx Certified
- Earth Reels & Ground Monitoring Units
- Explosion-Proof Bonding Accessories
ATEX Doors
ATEX-certified doors provide secure and explosion-resistant access for hazardous areas. Designed for use in Zone 1 and Zone 2 classified environments, these doors ensure safety and containment in chemical plants, refineries, and offshore installations.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: Dynaco
- Explosion-Resistant Steel Doors
- Gas-Tight & Fire-Rated Door Systems
- ATEX & IECEx Approved Construction

Motor Starters
ATEX motor starters deliver reliable motor control and protection in explosive gas and dust atmospheres. Certified for Zone 1 and Zone 2 environments, these flameproof and increased safety enclosures integrate contactors, overload relays, and isolators for safe operation.
Market-Leading Manufacturers: PEPPERL+FUCHS
- DOL & Star-Delta Starters – Ex d / Ex e Certified
- Explosion Proof Enclosures – Cast Aluminium or GRP
- ATEX & IECEx Approved Motor Control Solutions
Selection Of Hazardous Area Equipment
When selecting hazardous area equipment, it is vital to carry out a comprehensive area inspection and confirm that the correct zone classification has been identified.
Misclassifying a Zone 1 or Zone 0 environment as Zone 2 can lead to serious safety and operational risks.
Read more
All electrical and mechanical equipment installed in hazardous areas must be certified as intrinsically safe for use within the specified zone.
Products should carry the correct ATEX or IECEx certification — or local equivalents — depending on the country of installation.
Using the proper certified products helps ensure that ignition sources are controlled and that installations comply with safety legislation.
Safety Parameters When Working Within A Hazardous Area
The ignition temperature of flammable gases and vapours is the lowest temperature at which they can ignite.
Any equipment used in hazardous locations must have a maximum surface temperature lower than this ignition point to prevent explosions.
To simplify compliance, all certified devices are assigned a temperature class (T1–T6) that defines the maximum temperature the device can reach under standard operating conditions.
Read our in-depth guide on Temperature Classification
Working Within Hazardous Area Industries
Hazardous areas are found across many industries, including oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and food manufacturing.
Due to the risk of explosion from flammable gases or dusts, precise product specification and ongoing safety management are essential.
Read more
The oil and gas sector is among the most tightly regulated, requiring strict compliance with explosion protection standards.
Incorrect zoning or product misuse can result in severe incidents, legal consequences, and costly fines.
Hazards can also occur during transportation or maintenance operations, where volatile vapours or dust clouds may be present.
Using ATEX- and IECEx-certified equipment helps mitigate risk and ensures worker safety in such environments.
One notable example is the Deepwater Horizon disaster, which resulted in extensive human, environmental, and financial losses.
The event underscores the critical importance of effective hazardous area classification and safe equipment use.
Hazardous Area Zones FAQs
Q: Why are Hazardous Area Zones important?
A: Hazardous Area Zones are vital for identifying locations with explosive gases or dusts. Correct zoning ensures the use of certified ATEX and IECEx equipment, protecting workers, assets, and facilities from ignition risks. Accurate classification is essential for safety compliance and explosion prevention in industrial environments.
Q: What are all of the Hazardous Area Zones?
A: Hazardous Area Zones are divided into gas and dust categories — Zone 0, 1, and 2 for gases, and Zone 20, 21, and 22 for dusts. Each zone defines how often an explosive atmosphere is likely to occur, guiding equipment selection and safety design.
Q: What is an example of a Hazardous Area Zone?
A: A common example of a Hazardous Area Zone is a refinery or chemical plant, where flammable gases or vapours are present. For instance, Zone 1 areas may contain explosive atmospheres during normal operation — requiring certified ATEX lighting, enclosures, and equipment for safety.




























